In electrocardiography this part of an EKG includes at least one of the waves that it is named after. As the ECG trace is recorded there are a series of upwards and downwards deflections created that represents atrial and ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation.
As with every EZmed blog the material below will be presented simply and concisely.
. Small P wave occurs with depolarization of the. The deflection waves in an ECG tracing include. The components of a typical ECG tracing consist of three deflection waves which can be divided into segments and intervals.
This post will walk you through the different parts of an EKG wave and how it applies to one cycle of the conduction system of the heart. The deflection on the ECG that is a result of atrial depolarization. The waves on an ECG include the P wave Q wave R wave S wave T wave and U wave.
The P wave which is present only in patients who have had a heart attack. Each deflection aka. The QRS complex reflects the depolarization activation contraction of the ventricles.
The height of the deflection represents the amount of electrical activity flowing in that direction ie. A wave of depolarization traveling towards a positive EKG electrode causes which type of deflection on the EKG tracing. The higher the deflection the greater the amount of electrical activity flowing towards the lead.
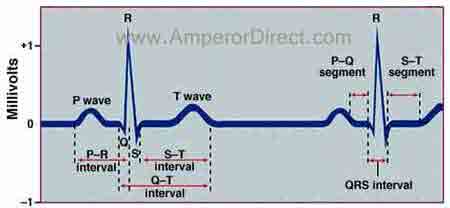
The first wave the small P wave lasts about 0. Label the waves segments and intervals of a normal ECG tracing shown below. A typical EKG.
The deflection waves of an ECG correlate to electrical changes either depolarization or repolarization of the hearts chambers. Thus when measuring the amplitude of a wave on the ECG the PR segment is the baseline. A positive or negative deflection from baseline indicates a specific electrical event.
View Available Hint s Reset Help P wave P wave QRS complex QRS complex T wave T wave P-R interval P-R interval S-T segment S-T segment Q-T interval Q-T. The deflection on the ECG that is a result of a ventricular repolarization. This is simply a section of baseline which is between the waves that it is named after.
08 s Marieb Mitchell 2010. Explore the purpose of an ECG the three wave types and. The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG.
An electrocardiogram ECG records the flow of electrical current on three distinct waves. Match the electrical events in the heart with the waves segments and intervals of a normal ECG tracing. Notice that there are several deflections from the isoelectric point that occur during the cycle.
The PQRS complex which follows ventricular contraction. Each deflection is referred to as a wave and each wave is labeled with a letter. The sequence of excitation of the heart related to deflection waves of an ECG tracing.
These are known as the ECG waves. A normal ECG tracing has three very characteristic deflections or waves called the P wave the QRS complex and the T waveThese deflections represent the electrical activity that regulates the contraction or relaxation of the atria or ventricles. The image above shows a typical EKG.
Although it may not always include a Q-wave R-wave and S-wave it is still referred to as a QRS complex. The deflection waves in an ECG tracing include the T wave which indicates ventricular repolarization The effect of endurance-type athletic training may be to. The time between two specific ECG events.
Wave on the ECG represents the average direction of electrical travel which is calculated using mathematical formulae by the ECG machine. The relationship between the deflections waves of an ECG and sequential excitation of the heart is shown below The Biology corner 2011 Figure1. P-R interval T wave Q-T interval S-T segment P wave QRS complex.
Refer to Figure 1. Depolarization describes the electrical activity that triggers contraction of the heart muscle. The deflection waves in an ECG tracing include A the P wave which is present from BSC bsc 2094c at Seminole State College of Florida.
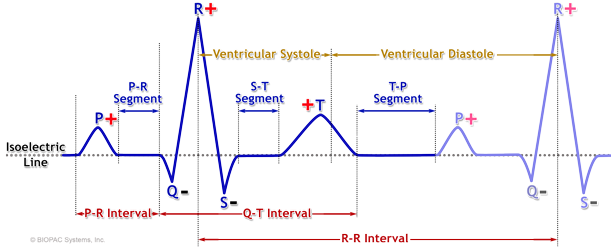
The main components of an EKG wave include the P wave PR segment QRS complex ST segment T wave and TP segment. It is a small smooth-contoured wave and represents atrial depolarisation. The Q-T interval which indicates the time of atrial contraction.
A region on an ECG tracing that between two waves but doesnt include a wave. The deflection on the ECG that is a result of ventricular depolarization. The T wave which indicates ventricular repolarization.

An Electrocardiogram Tracing Lead 1 Illustrating The Three Normally Download Scientific Diagram

How To Read An Ekg Electrocardiograph Pr Interval Medical Library Ekg
0 Comments